Edge computing
Edge computing is a technology that involves processing and analyzing data at the edge of a network, rather than in a centralized location. This approach allows for faster and more efficient data processing, as well as the ability to handle data in real-time. Edge computing can be used in a wide range of industries and applications, including the Internet of Things (IoT), autonomous vehicles, and industrial automation.
The traditional approach to data processing is to send all data to a centralized location, such as a data center, where it is processed and analyzed. However, this approach has several limitations, including latency, bandwidth constraints, and the cost of transmitting large amounts of data. Edge computing addresses these limitations by processing and analyzing data at the edge of the network, closer to where the data is generated.
One of the key advantages of edge computing is that it enables real-time data processing and analysis. This is particularly useful in applications such as autonomous vehicles, where decisions need to be made quickly based on sensor data. By processing data at the edge, decisions can be made in real-time, without the need to send data to a centralized location for processing.
Another advantage of edge computing is that it can help reduce the load on centralized data centers. By processing data at the edge, less data needs to be transmitted to centralized locations, reducing the load on data centers and decreasing the cost of data transmission.
Edge computing also helps to improve the security of data, as data is processed and analyzed at the edge, rather than being transmitted to a centralized location. This reduces the risk of data breaches and cyber-attacks, as data is not transmitted over the internet.
Edge computing is also useful in IoT applications, as it allows for the efficient processing and analysis of sensor data. This is particularly useful in industrial automation, where large amounts of sensor data need to be processed in real-time to control and monitor industrial processes.
Overall, edge computing is a technology that is becoming increasingly important as the amount of data being generated continues to grow. Edge computing can help to improve the speed, efficiency, security and cost of data processing, making it an essential technology for the Internet of Things (IoT), autonomous vehicles, and industrial automation.
History
The concept of edge computing has its roots in the early days of computing, when mainframe computers were used to process data. These computers were large and expensive, and data had to be sent to them for processing. This approach was known as centralized computing.
In the 1980s, personal computers and local area networks (LANs) began to emerge, allowing for decentralized computing, where data could be processed on individual computers rather than being sent to a central location. This approach was known as client-server computing.
In the early 2000s, the advent of cloud computing brought a new approach to data processing, where data and computational resources were stored and managed in remote data centers, and accessed over the internet. This approach was known as cloud computing, and it became increasingly popular as it allowed for easy access to computational resources and the ability to store and process large amounts of data.
In recent years, the growth of IoT and the increasing amount of data being generated has led to the emergence of edge computing. Edge computing is a distributed computing paradigm that brings computation and data storage closer to the devices that generate the data. This approach allows for faster and more efficient data processing, as well as the ability to handle data in real-time.
The history of edge computing is closely tied to the evolution of the internet and the increasing amount of data being generated. The evolution from centralized computing to cloud computing and now edge computing reflects a shift in the way data is processed and stored. Edge computing is the latest evolution in this process, as it allows for the efficient processing and analysis of data at the edge of a network.
Overall, the history of edge computing is closely tied to the evolution of the internet, and the increasing amount of data being generated. Edge computing is the latest evolution in the way data is processed and stored, which allows for faster and more efficient data processing and the ability to handle data in real-time.
How edge computing works?
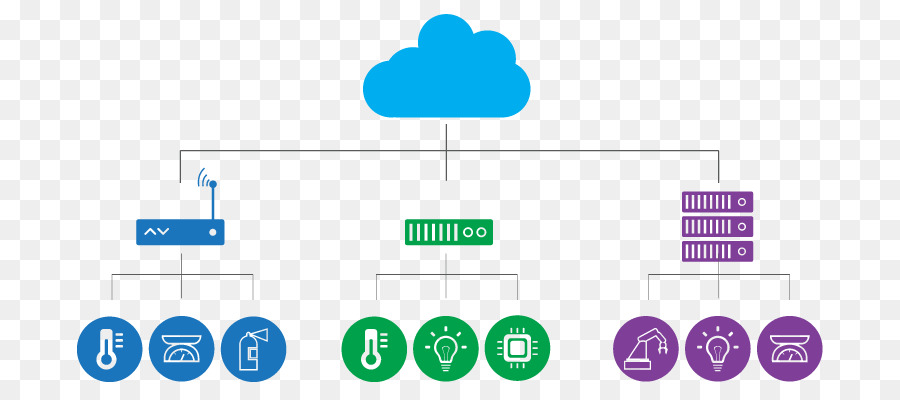
Edge computing works by bringing computation and data storage closer to the devices that generate the data, rather than relying on centralized data centers. This approach allows for faster and more efficient data processing, as well as the ability to handle data in real-time.
In edge computing, data is first generated by IoT devices such as sensors, cameras, and other connected devices. This data is then sent to edge devices, such as gateways or edge servers, which are located close to the devices that generate the data. The edge devices process and analyze the data, and then send it to a centralized location, such as a data center, for further processing and analysis.
The edge devices typically have a small amount of storage and computational capacity, which allows them to perform basic processing and analysis of the data. This can include tasks such as filtering, compression, and encryption. The edge devices also typically have a low latency, which allows them to process and analyze data in real-time.
Once the data has been processed and analyzed at the edge, it can then be sent to a centralized location, such as a data center, for further processing and analysis. This can include tasks such as machine learning, data visualization, and long-term storage.
Overall, edge computing works by bringing computation and data storage closer to the devices that generate the data, rather than relying on centralized data centers. This approach allows for faster and more efficient data processing, as well as the ability to handle data in real-time.
Types of edge computing
There are several types of edge computing, each with its own unique characteristics and uses:
- Mobile Edge Computing (MEC) – This type of edge computing involves processing data at the edge of the network, on mobile devices such as smartphones or tablets. MEC allows for faster and more efficient data processing, as well as the ability to handle data in real-time.
- Fog computing – This type of edge computing is similar to MEC, but it takes place at the edge of the network, on devices such as routers, switches, and gateways. Fog computing is particularly useful in industrial and manufacturing environments, where it can be used to control and monitor industrial processes in real-time.
- Multi-access Edge Computing (MEC) – This type of edge computing involves processing data at the edge of the network, on devices such as base stations, cellular towers, and other access points. MEC allows for faster and more efficient data processing, as well as the ability to handle data in real-time.
- Intelligent Edge – This type of edge computing is characterized by the integration of advanced technologies such as AI and machine learning to enable data processing, analysis and decision making at the edge. This allows for real-time decision making, reducing the need for sending data to a central location for processing
- Industrial Edge – This type of edge computing is designed for industrial and manufacturing environments, where it can be used to control and monitor industrial processes in real-time.
- Edge Virtualization – This type of edge computing involves creating virtualized environments at the edge of the network, allowing for the deployment and management of multiple virtual machines and containers. This allows for greater flexibility and scalability in edge computing environments.
Overall, there are several types of edge computing, each with its own unique characteristics and uses. Some of the most common types of edge computing include mobile edge computing, fog computing, multi-access edge computing, industrial edge, intelligent edge and edge virtualization. Each type has its own advantages and is suitable for specific use cases.
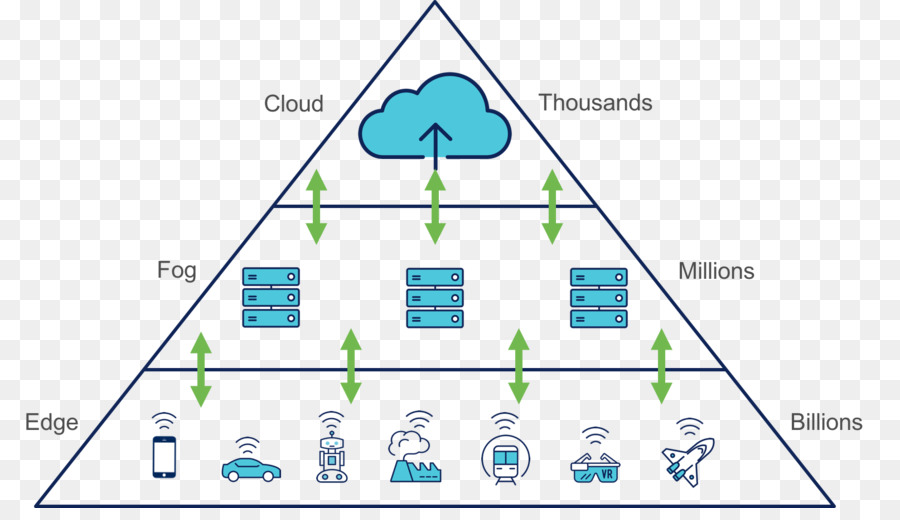
Application of edge computing
Edge computing has a wide range of applications across various industries, some of the most common applications include:
- Internet of Things (IoT) – Edge computing is particularly useful in IoT applications, as it allows for the efficient processing and analysis of sensor data. This is particularly useful in industrial automation, where large amounts of sensor data need to be processed in real-time to control and monitor industrial processes.
- Autonomous vehicles – Edge computing allows for real-time processing and analysis of sensor data in autonomous vehicles, which is necessary for making decisions in real-time.
- Industrial Automation – Edge computing can be used in industrial automation to control and monitor industrial processes in real-time. This can include tasks such as monitoring and controlling machinery, as well as monitoring and controlling industrial environments.
- Video Analytics – Edge computing can be used in video analytics to process and analyze video data in real-time, which can be used for tasks such as surveillance, facial recognition, and object detection.
- Smart Cities – Edge computing can be used in smart cities to process and analyze data in real-time, which can be used for tasks such as traffic management, energy management, and environmental monitoring.
- Healthcare – Edge computing can be used in healthcare to process and analyze medical data in real-time, which can be used for tasks such as patient monitoring, medical imaging, and telemedicine.
- Retail – Edge computing can be used in retail to process and analyze data in real-time, which can be used for tasks such as inventory management, customer behavior analysis, and real-time pricing optimization.
- Robotics – Edge computing can be used in robotics to process and analyze data in real-time, which can be used for tasks such as motion control, object detection, and machine vision.
- Gaming – Edge computing can be used in gaming to process and analyze data in real-time, which can be used for tasks such as game physics, artificial intelligence, and real-time rendering.
Overall, edge computing has a wide range of applications across various industries, including Internet of Things (IoT), autonomous vehicles, industrial automation, video analytics, smart cities, healthcare, retail, robotics, and gaming. Edge computing allows for faster and more efficient data processing, as well as the ability to handle data in real-time, which makes it useful in many applications.
Advantages
Edge computing has several advantages, including:
- Low Latency: Edge computing allows for faster and more efficient data processing, as data is processed at the edge of the network, closer to where it is generated. This reduces the latency associated with transmitting data to a centralized location for processing.
- Real-time Processing: Edge computing allows for real-time processing and analysis of data, which is particularly useful in applications such as autonomous vehicles and industrial automation where decisions need to be made quickly based on sensor data.
- Reduced Load on Centralized Data Centers: By processing data at the edge, less data needs to be transmitted to centralized locations, reducing the load on data centers and decreasing the cost of data transmission.
- Improved Security: Edge computing can help to improve the security of data, as data is processed and analyzed at the edge, rather than being transmitted to a centralized location. This reduces the risk of data breaches and cyber-attacks, as data is not transmitted over the internet.
- Cost-effective: Edge computing is cost-effective as it reduces the need for expensive and large data centers, and also reduce the cost of data transmission.
- Better Scalability: Edge computing allows for better scalability as the edge devices can be added or removed as per the requirement and also allows for distributed processing.
- Reliability: Edge computing improves the reliability of data processing, as the data is processed at the source and reduces the chances of data loss during transmission.
- Improved User Experience: Edge computing improves user experience by providing low latency and real-time processing which is particularly important for applications such as gaming and augmented reality.
Disadvantages
dge computing also has some disadvantages, including:
- Limited Resources: Edge devices have limited computational and storage resources, which can limit their ability to process and analyze large amounts of data.
- Security Risks: Edge devices can be vulnerable to security breaches and cyber-attacks, as they are typically connected to the internet and may not have the same level of security as centralized data centers.
- Complexity: Edge computing can be complex to set up and manage, particularly in large-scale deployments.
- Limited Expertise: Edge computing requires specialized skills and expertise, which can be difficult to find, particularly in smaller organizations.
- Cost: Edge computing can be expensive as it requires specialized hardware and software, as well as the cost of maintaining and updating edge devices.
- Limited Interoperability: Edge devices may be based on different platforms, which can make it difficult to share data and collaborate between different devices.
- Limited standardization: There is currently limited standardization in the edge computing industry, which can make it difficult to compare and choose between different edge devices and platforms.
- Limited Redundancy: Edge computing has limited redundancy as the data is processed at the edge and in case of any failures, the data can be lost.
Edge computing in India
Edge computing is a relatively new technology in India, but it is gaining popularity as the country looks to digitalize various industries and improve its technology infrastructure. The growth of Internet of Things (IoT) and the increasing amount of data being generated in India has led to a growing interest in edge computing.
The Indian government is investing in the development of edge computing through initiatives such as the Digital India program, which aims to connect all citizens to the internet and promote the use of technology in various sectors. The Indian government is also focusing on initiatives such as 5G and Industry 4.0, which are expected to boost the growth of edge computing in India.
In the private sector, major Indian companies such as Tata Communications, Wipro, and Tech Mahindra are investing in edge computing and developing solutions for various industries such as manufacturing, transportation, and healthcare.
In the manufacturing sector, companies are using edge computing to improve efficiency and productivity, by monitoring and controlling industrial processes in real-time. In the transportation sector, companies are using edge computing to improve safety and efficiency in autonomous vehicles.
In the healthcare sector, companies are using edge computing to improve patient care and telemedicine, by monitoring and analyzing medical data in real-time.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Edge computing is a relatively new technology that is gaining popularity as a way to process and analyze data at the edge of the network, closer to where it is generated. This allows for faster and more efficient data processing, as well as the ability to handle data in real-time. Edge computing has a wide range of applications across various industries, including Internet of Things (IoT), autonomous vehicles, industrial automation, video analytics, smart cities, healthcare, retail, robotics, and gaming.
Edge computing has several advantages such as low latency, real-time processing, reduced load on centralized data centers, improved security, cost-effective, better scalability, reliability and improved user experience. However, it also has some disadvantages such as limited resources, security risks, complexity, limited expertise, cost, limited interoperability, limited standardization and limited redundancy.
Edge computing is also seeing significant growth in India, as the country looks to improve its technology infrastructure and digitalize various industries. The Indian government and private sector companies are investing in the development of edge computing and developing solutions for various industries such as manufacturing, transportation, and healthcare. With the growing amount of data being generated, edge computing is becoming increasingly important in various industries and will likely continue to play a significant role in the technology landscape in the future.
![]()