Internet of Things (IoT)
The Internet of Things (IoT) is a rapidly growing field that involves the integration of internet connectivity into everyday objects and devices. This allows these objects to collect and share data, enabling them to communicate with one another and with other devices, such as smartphones and computers.
One of the key features of IoT is the ability to collect and analyze large amounts of data, which can be used to improve efficiency, productivity, and safety in a wide range of industries. For example, in the field of smart homes, IoT-enabled devices such as smart thermostats, lights, and security systems can be used to control and monitor the home, making it more comfortable and energy-efficient. Similarly, in the field of smart cities, IoT-enabled devices such as traffic sensors, air quality monitors, and waste management systems can be used to improve the efficiency and sustainability of cities.

IoT is also playing a major role in the field of transportation, with the development of connected cars, intelligent traffic systems, and smart logistics. These systems can improve road safety, reduce traffic congestion, and optimize the use of resources.
Another important application of IoT is in the field of healthcare. IoT-enabled devices such as wearable health monitors and medical equipment can be used to improve patient outcomes and make healthcare more efficient and cost-effective. In agriculture, IoT-enabled devices such as drones, sensors, and cameras can be used to improve crop yields and reduce waste.
The industrial sector is also benefiting from IoT, with the use of IoT-enabled devices, such as sensors, cameras and robots, to improve efficiency, productivity, and safety in manufacturing and logistics.
Despite the many potential benefits of IoT, there are also concerns about its impact on society. One concern is the security of IoT-enabled devices, as they can be vulnerable to hacking and cyber attacks. There are also concerns about the privacy of data collected by IoT devices, particularly if the data is sensitive or personal.
How IoT works
The Internet of Things (IoT) works by connecting everyday objects and devices to the internet, allowing them to collect and share data, and communicate with one another and other devices, such as smartphones and computers.
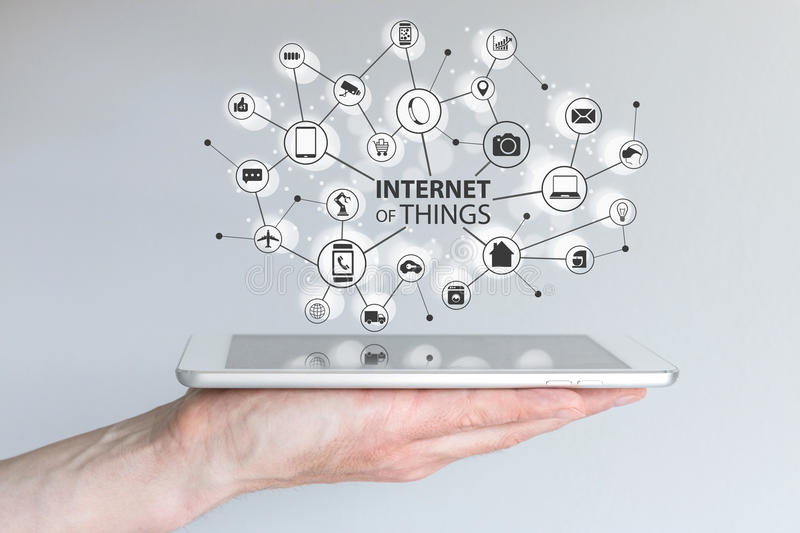

An IoT system typically consists of three main components:
- IoT-enabled devices or “things”: These are the physical objects and devices that are connected to the internet. These devices are equipped with sensors, actuators, and other electronic components that allow them to collect and share data. Examples of IoT-enabled devices include smart thermostats, connected cars, and wearable health monitors.
- Network infrastructure: This is the network of devices, gateways, and communication protocols that allow IoT-enabled devices to connect to the internet and to one another. This infrastructure can include a variety of technologies, such as Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, and cellular networks.
- Cloud or on-premises platform: This is the software platform that allows for the management, storage, and analysis of data collected by IoT-enabled devices. The platform can also be used to create and run applications that can control and monitor the devices.
IoT-enabled devices collect data through sensors, which are then sent over the network infrastructure to the cloud or on-premises platform. The data can then be analyzed, stored, and used for various purposes, such as controlling the device, making decisions, and generating insights.
IoT systems can also include additional components such as edge computing, which allows for data processing and analysis closer to the source, reducing the need for cloud processing and minimizing delay.
Application of IoT
The Internet of Things (IoT) has the potential to revolutionize many aspects of our lives, with applications in a wide range of industries and fields. Some of the key applications of IoT include:
- Smart homes: IoT-enabled devices such as smart thermostats, lights, and security systems can be used to control and monitor the home, making it more comfortable and energy-efficient. Smart home devices can also be integrated with smart home hubs, allowing for easy control through smartphones and voice assistants.
- Smart cities: IoT-enabled devices such as traffic sensors, air quality monitors, and waste management systems can be used to improve the efficiency and sustainability of cities. Smart cities also use IoT for public safety, providing real-time surveillance and emergency response systems.
- Industrial IoT: IoT-enabled devices such as sensors, cameras, and robots can be used to improve efficiency, productivity, and safety in industries such as manufacturing, logistics, and agriculture. Industrial IoT can also be used to optimize resource usage, reduce downtime and improve maintenance.
- Healthcare: IoT-enabled devices such as wearable health monitors, medical equipment and smart pill dispensers can be used to improve patient outcomes and make healthcare more efficient and cost-effective. IoT also allows remote monitoring of patients, which is particularly useful for elderly or chronically ill patients.
- Transportation: IoT-enabled devices such as connected cars, intelligent traffic systems, and smart logistics can be used to improve road safety, reduce traffic congestion, and optimize the use of resources. IoT can also be used in public transportation, providing real-time tracking and improving the passenger experience.
- Retail: IoT-enabled devices such as RFID tags, beacons, and smart shelves can be used to improve inventory management, track customer movements and personalize the shopping experience. IoT also allows for real-time monitoring of store conditions such as temperature and lighting.
- Energy: IoT-enabled devices such as smart meters, energy management systems, and solar panels can be used to optimize energy usage, reduce waste and improve overall energy efficiency.
- Agriculture: IoT-enabled devices such as drones, sensors, and cameras
Advantages of IoT
The Internet of Things (IoT) has the potential to bring many benefits to society, including:
- Increased Efficiency and Productivity: IoT-enabled devices can automate tasks and gather data, allowing for improved decision-making and increased efficiency and productivity in a wide range of industries.
- Improved Decision-Making: IoT-enabled devices can gather and analyze large amounts of data, allowing for more informed and accurate decision-making in fields such as healthcare, finance, transportation and agriculture.
- Real-time monitoring and control: IoT-enabled devices allow for real-time monitoring and control of various systems such as homes, cities, industries and transportation, leading to improved safety and efficiency.
- Cost savings: IoT-enabled devices can optimize resource usage and reduce waste, leading to cost savings in various industries.
- Improved safety: IoT-enabled devices can be used to monitor and predict potential safety hazards, such as traffic congestion or equipment failures, leading to improved safety in transportation and other industries.
- Predictive Maintenance: IoT-enabled devices can be used to predict and prevent equipment failures, leading to decreased downtime and increased efficiency in manufacturing and other industries.
- Personalization: IoT-enabled devices can be used to personalize products and services to individual customers, leading to improved customer experiences and increased satisfaction.
- Connectivity: IoT allows for the connectivity of various devices, systems and even entire cities, leading to more efficient and seamless communication and coordination.
- Sustainable development: IoT-enabled devices can be used to optimize resource usage and reduce waste in industries such as agriculture and energy, leading to sustainable development.
- Remote monitoring and control: IoT-enabled devices allow for remote monitoring and control of various systems, leading to improved efficiency and accessibility in many industries.
- Automation of repetitive tasks: IoT-enabled devices can automate repetitive and time-consuming tasks, freeing up human workers to focus on more complex and creative tasks.
Disadvantages of IoT
While the Internet of Things (IoT) has the potential to bring many benefits, it also has several potential downsides, including:
- Security concerns: IoT-enabled devices can be vulnerable to hacking and cyber attacks, which can compromise personal and sensitive information, and cause significant harm to individuals or organizations.
- Privacy concerns: The collection and analysis of large amounts of data by IoT devices can raise privacy concerns, particularly if the data is sensitive or personal.
- Dependence on technology: Relying too much on IoT-enabled devices can lead to a decrease in human skills and judgment, making it difficult for people to function without the help of technology.
- Job displacement: As IoT-enabled devices become more advanced, they may be able to automate tasks that were previously done by humans, leading to job loss and economic inequality.
- Limited scalability: IoT-enabled devices can generate a large amount of data which can be difficult to process and analyze, limiting their scalability.
- Limited interoperability: IoT-enabled devices can be built with different standards and protocols, which can make it difficult for them to communicate with one another.
- Limited battery life: IoT-enabled devices are often battery-powered, which can limit their lifespan, and make them difficult to maintain.
- Limited accuracy: IoT-enabled devices can have limited accuracy, which can lead to inaccurate data and incorrect decision-making.
- Limited generalization: IoT-enabled devices are only able to generalize well on similar data they have seen during training, which can be a problem if the test data is different from the training data.
- Ethical concerns: IoT-enabled devices can raise ethical concerns if they are used to make life-or-death decisions, such as in the case of autonomous weapons, or if they are used to control or manipulate human behavior.
- Lack of standardization: IoT-enabled devices can be built with different standards and protocols, which can make it difficult for them to communicate with one another, and for developers to create interoperable solutions.
Conclusion on Internet of Things (IoT)
In conclusion, the Internet of Things (IoT) is a rapidly growing field that has the potential to revolutionize many aspects of our lives. IoT-enabled devices can be used to improve efficiency, productivity, and safety in a wide range of industries, from smart homes and cities, to healthcare and transportation. IoT-enabled devices can also be used to optimize resource usage, reduce waste and improve overall energy efficiency.
However, there are also concerns about the impact of IoT on society, particularly in regards to security, privacy, and job displacement. It is important to develop security and privacy standards for IoT-enabled devices and to be transparent about the data being collected. Additionally, it is crucial to take into account ethical considerations and to develop guidelines for the responsible use of IoT technology.
Overall, the IoT has the potential to bring significant benefits to society, but it is important to be aware of the potential downsides and to take steps to mitigate them. As the field of IoT continues to evolve, it will be important to monitor and address these concerns to ensure that the technology is used in a responsible and ethical manner.
![]()


Pingback: Edge computing & its applications - Tech Navigator